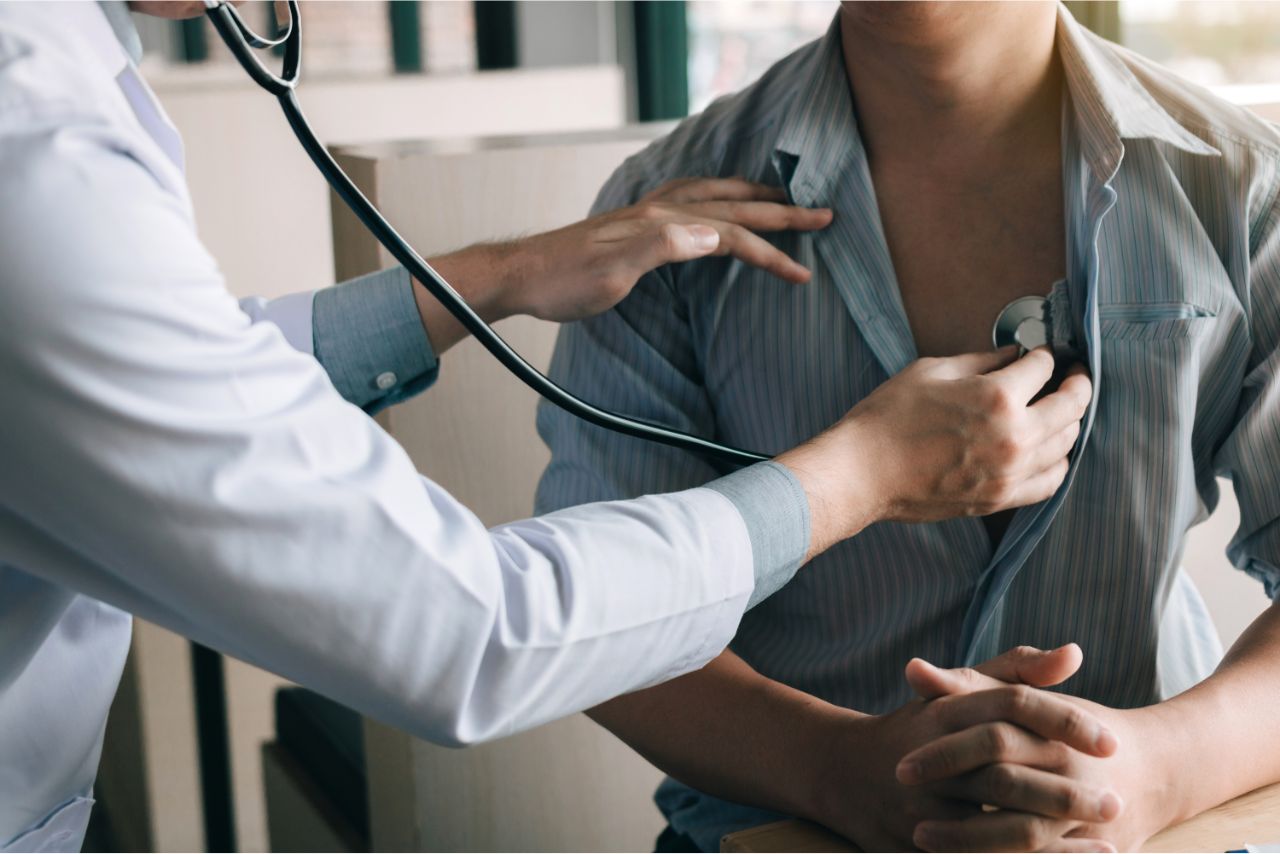
Do you know how alcohol affects your cardiovascular health?
Discover the 9 best ways it can impact your heart and blood vessels.
From increased blood pressure and elevated heart rate to the risk of arrhythmias and weakened heart muscles, alcohol can take a toll on your cardiovascular system.
Learn more about these effects and how they can potentially lead to serious conditions like blood clots, atherosclerosis, stroke, impaired heart function, and higher risk of heart disease.
Stay informed to prioritize your heart health.
Increased Blood Pressure
If you regularly consume alcohol, it can lead to an increase in your blood pressure. Alcohol consumption has been linked to elevated blood pressure levels, which can have detrimental effects on your cardiovascular health. When you drink alcohol, it causes your blood vessels to constrict, resulting in higher blood pressure readings. This constriction puts additional strain on your heart and can lead to long-term damage.
Alcohol-induced increases in blood pressure can also be accompanied by an elevated heart rate. When alcohol is present in your system, it can stimulate the release of stress hormones, such as adrenaline, which can cause your heart to beat faster. This increased heart rate combined with elevated blood pressure can put a significant strain on your cardiovascular system.
Moreover, alcohol consumption can also lead to alcohol-induced irregular heartbeats, known as arrhythmias. These irregular heart rhythms can disrupt the normal flow of blood and oxygen to your organs, further increasing your risk of heart problems.
It is important to note that the effects of alcohol on blood pressure can vary from person to person. Factors such as overall health, genetics, and the amount and frequency of alcohol consumed can all play a role in determining the impact on blood pressure levels. Therefore, it's crucial to be aware of the potential risks and to moderate your alcohol consumption to maintain a healthy blood pressure.
Elevated Heart Rate
Alcohol consumption can lead to an elevated heart rate, which can have negative effects on cardiovascular health. Increased blood pressure is one of the main factors contributing to this elevated heart rate.
Additionally, alcohol can increase the risk of arrhythmias and impair heart function. These effects highlight the importance of moderation and awareness when it comes to alcohol consumption for maintaining a healthy heart.
Increased Blood Pressure
Your increased blood pressure and elevated heart rate can be directly attributed to alcohol's effects on your cardiovascular health. When you consume alcohol, it can lead to a temporary rise in blood pressure. This occurs because alcohol causes blood vessels to constrict, making it harder for blood to flow through them.
Additionally, alcohol stimulates the release of stress hormones, such as adrenaline, which can further increase your heart rate and blood pressure.
Over time, chronic alcohol consumption can have more serious effects on your cardiovascular system. It can lead to long-term hypertension, which increases the risk of heart disease and stroke. Furthermore, excessive alcohol intake can contribute to the development of other cardiovascular conditions, such as arrhythmias and cardiomyopathy.
It's important to be mindful of your alcohol consumption and its potential impact on your cardiovascular health.
Risk of Arrhythmias
As you continue consuming alcohol, it can increase your risk of experiencing arrhythmias, specifically an elevated heart rate. Alcohol affects the electrical signals in your heart, disrupting the normal rhythm and causing irregular heartbeats.
Here are some key points to consider regarding arrhythmia prevention and management:
- Limit your alcohol intake: Reducing or avoiding alcohol can help prevent arrhythmias.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and managing stress can reduce your risk of arrhythmias.
- Seek medical advice: If you have a history of arrhythmias or other heart conditions, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
- Follow prescribed medications: If you're taking medications for arrhythmia management, make sure to take them as instructed by your doctor.
Impaired Heart Function
Limiting alcohol consumption can help prevent impaired heart function, specifically an elevated heart rate. When consumed in excess, alcohol can have a detrimental impact on heart rhythm, leading to an increased heart rate. This can put additional strain on the heart, potentially leading to long-term damage.
Alcohol affects the autonomic nervous system, which controls heart rate, causing it to become irregular. The exact mechanism behind this isn't fully understood, but it's believed that alcohol disrupts the electrical signals that regulate heart rhythm.
The risk of impaired heart function is particularly significant for individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions. Therefore, it's crucial to be mindful of alcohol consumption to maintain a healthy heart rhythm and overall cardiovascular health.
Risk of Arrhythmias
Alcohol consumption can have a significant impact on your heart rhythm, increasing the risk of arrhythmias.
One of the ways alcohol affects the heart is by inducing irregular heartbeats, which can disrupt the normal electrical signals that control your heartbeat.
This can lead to palpitations and potentially more serious arrhythmias.
Alcohol-Induced Irregular Heartbeats
To reduce the risk of arrhythmias caused by alcohol consumption, it's important to be aware of the effects it can have on your cardiovascular health. Alcohol-induced irregular heartbeats, also known as arrhythmias, can occur due to excessive alcohol consumption. Here are some important points to consider:
- Alcohol can disrupt the electrical signals in your heart, leading to irregular heart rhythms.
- Heavy drinking can increase the risk of atrial fibrillation, a common type of arrhythmia.
- Alcohol can also trigger premature ventricular contractions (PVCs), which are extra, abnormal heartbeats.
- The risk of arrhythmias is higher in individuals with existing heart conditions or a history of arrhythmias.
By understanding the impact of alcohol on your heart health, you can make informed decisions and take steps to reduce the risk of alcohol-induced arrhythmias.
It's always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance on alcohol consumption and its effects on your cardiovascular health.
Increased Risk of Palpitations
If you drink excessively, you run the risk of experiencing an increased frequency of palpitations, which can indicate the presence of arrhythmias. Alcohol can have a significant impact on your cardiovascular health, especially when it comes to palpitations.
When you consume alcohol, it can lead to dehydration, which can in turn affect the electrical impulses in your heart. This can result in irregular heartbeats and palpitations.
Additionally, alcohol can also interfere with the normal functioning of your heart during exercise. Alcohol consumption can impair your heart's ability to pump blood efficiently, leading to palpitations and an increased risk of arrhythmias during physical activity.
It's important to be mindful of the effects of alcohol on your cardiovascular health and to moderate your alcohol intake accordingly, especially when engaging in exercise and ensuring proper hydration.
Impact on Heart Rhythm
Excessive alcohol consumption can significantly impact your heart rhythm, increasing the risk of developing arrhythmias. When alcohol enters your bloodstream, it affects the electrical signals that regulate your heartbeat, leading to irregular heart rhythms.
Here are some key ways alcohol can impact your heart rhythm:
- Decreased heart rate variability: Alcohol can reduce the variation in time intervals between heartbeats, which is an important marker of heart health. This decreased variability can increase the risk of arrhythmias.
- Influence on cardiac conduction: Alcohol can disrupt the normal conduction of electrical impulses through the heart, causing abnormal heart rhythms. This interference with cardiac conduction can result in arrhythmias.
- Triggering atrial fibrillation: Alcohol consumption has been identified as a trigger for atrial fibrillation, a common type of arrhythmia characterized by rapid and irregular heartbeats.
- Increased risk of sudden cardiac death: Excessive alcohol intake has been associated with an increased risk of sudden cardiac death, which can be caused by fatal arrhythmias.
It is important to be aware of these effects and to consume alcohol in moderation to protect your cardiovascular health.
Weakened Heart Muscles
Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol can lead to weakened heart muscles, which can significantly impact your cardiovascular health. When you consume alcohol in large quantities, it can have a toxic effect on your heart cells, causing them to become damaged and weakened over time. This can result in a condition known as alcoholic cardiomyopathy, where the heart muscles become thin and floppy, reducing their ability to pump blood effectively.
Alcohol-induced cardiomyopathy is a serious condition that can lead to a range of cardiovascular problems. As the weakened heart muscles struggle to pump blood efficiently, it can result in symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling in the legs and ankles. In severe cases, it can even lead to heart failure, where the heart is unable to meet the body's demands for oxygen and nutrients.
The exact mechanism by which alcohol damages the heart muscles isn't fully understood, but it's believed to involve a combination of factors. Alcohol can directly affect the heart cells, interfering with their normal functioning and causing structural changes. Additionally, alcohol abuse is often associated with poor nutrition and vitamin deficiencies, which can further contribute to the weakening of the heart muscles.
To protect your cardiovascular health, it's important to consume alcohol in moderation or avoid it altogether. If you have a history of heavy alcohol consumption, it's advisable to seek medical advice to assess the potential impact on your heart health and to explore strategies for reducing the risk of further damage.
Formation of Blood Clots
When consuming alcohol, be aware of its potential to contribute to the formation of blood clots in your cardiovascular system. Alcohol can affect blood clot formation in several ways:
- Increased platelet aggregation: Alcohol can cause platelets, the cells responsible for blood clotting, to stick together more easily. This increased platelet aggregation can lead to the formation of blood clots.
- Impaired fibrinolysis: Fibrinolysis is the process by which blood clots are broken down. Alcohol can interfere with this process, resulting in decreased fibrinolysis and an increased risk of blood clot formation.
- Disruption of endothelial function: The endothelium is the inner lining of blood vessels. Alcohol can impair the function of the endothelium, leading to an imbalance in the production of certain substances that regulate blood clotting.
- Increased levels of certain clotting factors: Alcohol can increase the levels of certain clotting factors in the blood, making it more prone to clot formation.
It is important to note that moderate alcohol consumption may have some cardiovascular benefits. However, excessive or chronic alcohol consumption can outweigh these potential benefits and increase the risk of blood clot formation.
It's always recommended to speak with a healthcare professional to understand the potential risks and benefits of alcohol consumption for your specific cardiovascular health.
Atherosclerosis Development
Continuing from the previous subtopic on the formation of blood clots, alcohol consumption can also contribute to the development of atherosclerosis in your cardiovascular system.
Atherosclerosis is a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in your arteries, narrowing and hardening them over time. This can lead to various cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks and strokes.
Alcohol has a direct impact on your blood vessels, affecting their structure and function. It promotes the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, which is known as 'bad' cholesterol. Oxidized LDL cholesterol is more likely to adhere to the walls of your arteries, initiating the formation of plaque.
Additionally, alcohol interferes with the production and function of endothelial nitric oxide, a substance that helps regulate blood vessel dilation and constriction. Without proper nitric oxide levels, your blood vessels can become more rigid and less flexible, contributing to atherosclerosis development.
To prevent atherosclerosis, it's important to moderate your alcohol consumption. Excessive drinking can significantly increase your risk of developing this condition. It's recommended that men limit their alcohol intake to no more than two drinks per day, while women should consume no more than one drink per day.
Increased Risk of Stroke
Alcohol consumption can significantly increase your risk of experiencing a stroke, a serious cardiovascular event. This is due to the detrimental effects that alcohol has on the brain and blood vessels. Here are four ways in which alcohol can increase your risk of stroke:
- Increased risk of hemorrhage: Alcohol can thin the blood and impair the ability of blood to clot properly. This increases the risk of bleeding in the brain, leading to a hemorrhagic stroke.
- Alcohol-related brain damage: Chronic alcohol abuse can cause damage to the brain, including shrinking of brain cells and changes in brain structure. This can impair the brain's ability to regulate blood flow and increase the risk of stroke.
- High blood pressure: Alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure levels, increasing the strain on blood vessels and making them more prone to damage. High blood pressure is a major risk factor for stroke.
- Irregular heart rhythm: Excessive alcohol intake can disrupt the normal electrical signals in the heart, leading to an irregular heartbeat known as atrial fibrillation. This condition can increase the risk of blood clots forming in the heart, which can then travel to the brain and cause a stroke.
It is important to be aware of these risks and consume alcohol in moderation, if at all, to reduce your risk of stroke and maintain good cardiovascular health.
Impaired Heart Function
To further understand the effects of alcohol on cardiovascular health, it's important to consider how it impairs the function of your heart. Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to impaired cardiac function and alcohol-related heart damage. When you consume alcohol, it affects the electrical system of your heart, causing irregular heartbeats, known as arrhythmias. These arrhythmias can disrupt the normal pumping of blood, leading to a decrease in the heart's efficiency and potentially causing symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
Moreover, alcohol can weaken the heart muscle, a condition known as alcoholic cardiomyopathy. This occurs when the heart muscle becomes thinner and less able to contract effectively. As a result, the heart's pumping capacity diminishes, leading to symptoms such as fluid retention, swelling, and congestive heart failure.
Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption can increase blood pressure, putting added strain on the heart. High blood pressure can damage the arteries and increase the risk of heart disease.
It is worth noting that the effects of alcohol on heart function can vary depending on individual factors such as genetics, overall health, and the amount and duration of alcohol consumption. However, it's crucial to recognize that excessive alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on your heart's function and overall cardiovascular health.
Higher Risk of Heart Disease
Excessive alcohol consumption significantly increases your vulnerability to heart disease. It's important to understand the impact of alcohol on your cardiovascular health and take necessary steps to prevent heart disease.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Alcohol and high blood pressure: Consuming alcohol in excess can lead to high blood pressure, a major risk factor for heart disease. It's crucial to monitor and control your blood pressure levels through lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise and a healthy diet.
- Alcohol and cholesterol levels: Alcohol can raise your triglyceride levels, which is a type of fat in the blood. High triglyceride levels can contribute to the development of heart disease. To maintain healthy cholesterol levels, it's essential to limit alcohol intake and incorporate heart-healthy foods into your diet.
- Alcohol and weight gain: Alcohol is high in calories and can contribute to weight gain. Being overweight or obese increases your risk of heart disease. By moderating your alcohol consumption and adopting a balanced diet, you can manage your weight and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Alcohol and heart rhythm problems: Excessive drinking can disrupt the normal electrical signals in your heart, leading to irregular heart rhythms. These irregularities can increase the risk of stroke and heart failure. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption can help maintain a healthy heart rhythm.
To prevent heart disease, it's important to make lifestyle modifications such as limiting alcohol intake, maintaining a healthy weight, managing blood pressure levels, and adopting a heart-healthy diet. By taking these steps, you can significantly reduce your risk of heart disease and improve your overall cardiovascular health.
- Overcoming Emotional Intimacy Challenges With Alcohol Misuse - November 18, 2023
- Overcoming Alcohol's Impact on Emotional Intimacy: 13 Essential Tips - November 18, 2023
- 6 Ways to Overcome Emotional Intimacy Challenges With Alcohol - November 18, 2023